హైపోథైరాయిడిజం: కూర్పుల మధ్య తేడాలు
Pranayraj1985 (చర్చ | రచనలు) దిద్దుబాటు సారాంశం లేదు |
Pranayraj1985 (చర్చ | రచనలు) దిద్దుబాటు సారాంశం లేదు |
||
| పంక్తి 15: | పంక్తి 15: | ||
| diagnosis = [[Blood test]]s ([[thyroid-stimulating hormone]], [[thyroxine]])<ref name=NIH2016/> |
| diagnosis = [[Blood test]]s ([[thyroid-stimulating hormone]], [[thyroxine]])<ref name=NIH2016/> |
||
| differential = [[Depression (mood)|Depression]], [[dementia]], [[heart failure]], [[chronic fatigue syndrome]]<ref>{{cite book|last1=Ferri|first1=Fred F.|title=Ferri's differential diagnosis : a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders|date=2010|publisher=Elsevier/Mosby|location=Philadelphia, PA|isbn=978-0323076999|page=Chapter H|edition=2nd}}</ref> |
| differential = [[Depression (mood)|Depression]], [[dementia]], [[heart failure]], [[chronic fatigue syndrome]]<ref>{{cite book|last1=Ferri|first1=Fred F.|title=Ferri's differential diagnosis : a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders|date=2010|publisher=Elsevier/Mosby|location=Philadelphia, PA|isbn=978-0323076999|page=Chapter H|edition=2nd}}</ref> |
||
| prevention = [[iodised salt|Salt iodization]] |
| prevention = [[iodised salt|Salt iodization]] |
||
| treatment = [[Levothyroxine]]<ref name=NIH2016/> |
| treatment = [[Levothyroxine]]<ref name=NIH2016/> |
||
| medication = |
| medication = |
||
| prognosis = |
| prognosis = |
||
| frequency = 0.3–0.4% (USA) |
| frequency = 0.3–0.4% (USA) |
||
| deaths = |
| deaths = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
17:50, 18 అక్టోబరు 2020 నాటి కూర్పు
| Hypothyroidism | |
|---|---|
| పర్యాయపదాలు | Underactive thyroid, low thyroid, hypothyreosis |
 | |
| Molecular structure of thyroxine, the deficiency of which causes the symptoms of hypothyroidism | |
| ఉచ్ఛారణ | |
| ప్రత్యేకత | Endocrinology |
| లక్షణాలు | Poor ability to tolerate cold, feeling tired, constipation, depression, weight gain[3] |
| ఉపద్రవాలు | During pregnancy can result in cretinism in the baby[4] |
| సాధారణ ఆరంభం | < 60 years old[3] |
| కారణాలు | Iodine deficiency, Hashimoto's thyroiditis[3] |
| రోగనిర్ధారణ పద్ధతి | Blood tests (thyroid-stimulating hormone, thyroxine)[3] |
| భేదాత్మక నిర్ధారణ | Depression, dementia, heart failure, chronic fatigue syndrome[5] |
| నివారణ | Salt iodization |
| చికిత్స | Levothyroxine[3] |
| తరచుదనం | 0.3–0.4% (USA) |
హైపోథైరాయిడిజం, థైరాయిడ్ గ్రంథి తగినంత థైరాయిడ్ హార్మోన్ ను ఉత్పత్తి చేయనప్పుడు వచ్చే వ్యాధి. ఈ వ్యాధి ప్రభావంతో చలిని తట్టుకోలేకపోవడం, నీరసం, మలబద్దకం, హృదయ స్పందన రేటు తగ్గడం, నిరాశ, బరువు పెరగడం వంటి అనేక లక్షణాలలు కలుగుతాయి. కొన్నిసార్లు గ్రంథివాపు వ్యాధి కారణంగా మెడ ముందుభాగంలో వాపు ఏర్పడుతుంది.[3] గర్భధారణ సమయంలో హైపోథైరాయిడిజం చికిత్స చేయకపోతే పుట్టిన శిశువులో పెరుగుదల, మేధోవికాసం తగ్గడంతోపాటు పుట్టుకతో వచ్చే అయోడిన్ లోపం సిండ్రోమ్కు దారితీస్తుంది.[4]
తీసుకునే ఆహారంలో అయోడిన్ తక్కువగా ఉండడం హైపోథైరాయిడిజం రావడానికి అత్యంత ముఖ్య కారణం. థైరాయిడ్-స్టిమ్యులేటింగ్ హార్మోన్ (టిఎస్హెచ్), థైరాక్సిన్ స్థాయిలను కొలిచే రక్త పరీక్షలతో ఈ హైపోథైరాయిడిజం రోగ నిర్ధారణ చేయవచ్చు.
ఉప్పులో అయోడిన్ శాతాన్ని పెంచడం ద్వారా అనేకమందిలో ఈ హైపోథైరాయిడిజం నిరోధించబడింది. లెవోథైరాక్సిన్తో థైరాయిడ్ హార్మోన్ ను పెంచడం ద్వారా ఈ హైపోథైరాయిడిజానికి చికిత్స చేయవచ్చు. గర్భధారణ సమయంలో థైరాయిడ్ మందులు వాడడం శ్రేయస్కరం.
వ్యాధి లక్షణాలు
హైపోథైరాయిడిజం ఉన్నవారికి ప్రత్యేకంగా రోగ లక్షణాలు ఉండవు.. సాధారణంగా కనిపించే లక్షణాలు హైపోథైరాయిడిజంతో సంబంధాన్ని కలిగివుంటాయి.[6]
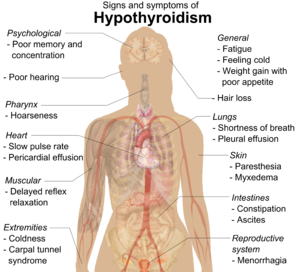
| లక్షణాలు[6] | సంకేతాలు |
|---|---|
| అలసట | పొడి, ముతక చర్మం |
| చలి | చల్లని శరీరభాగాలు |
| జ్ఞాపకశక్తి, ఏకాగ్రత తగ్గడం | చర్మంలో మ్యూకోపాలిసాకరైడ్ నిక్షేపాలు |
| మలబద్ధకం, అజీర్తి | జుట్టు రాలిపోవుట |
| బరువు పెరుగుతుంది | పల్స్ రేటు తగ్గడం |
| శ్వాస ఆడకపోవుట | అవయవాల వాపు |
| మొరటు గొంతు | స్నాయువు ప్రతిచర్యల తగ్గుదల |
| ఆడవారిలో అధిక ఋతుస్రావం | కార్పాల్ టన్నెల్ సిండ్రోమ్ |
| అసాధారణ సంచలనం | ప్లూరల్ ఎఫ్యూషన్, జలోదరం, పెరికార్డియల్ ఎఫ్యూషన్ |
| వినికిడి తగ్గడం |
గర్భదారణ సమయంలో
సబ్క్లినికల్ హైపోథైరాయిడిజం వల్ల సంతానలేమికి దారితీస్తుంది, కొన్నికొన్నిసార్లు గర్భస్రావం అయ్యే ప్రమాదం కూడా ఉంది. గర్భధారణ ప్రారంభంలో హైపోథైరాయిడిజం, ప్రీ-ఎక్లంప్సియా వల్ల తక్కువ తెలివితేటలతో ఉన్న సంతానం కలగడంకానీ, పుట్టిన సమయంలో శిశు మరణించే ప్రమాదం కలగవచ్చు. గర్భధారణలో 0.3–0.5% మహిళలు హైపోథైరాయిడిజం వ్యాధికి గురవుతున్నారు.
పిల్లలలో
హైపోథైరాయిడిజంతో బాధపడుతున్న పసి పిల్లలు సాధారణ జనన బరువు, ఎత్తు కలిగి ఉంటారు. కొంతమందిలో మగత, కండరాల స్థాయి తగ్గడం, గట్టిగా ఏడవడం, తినడంలో ఇబ్బందులు, మలబద్ధకం, నాలుక వెడల్పు అవడం, బొడ్డు హెర్నియా, పొడి చర్మం, శరీర ఉష్ణోగ్రత తగ్గడం, కామెర్లు వంటివి రావచ్చు. థైరాయిడ్ హార్మోన్ ఉత్పత్తి చేయని థైరాయిడ్ గ్రంథి ఉన్న పిల్లలలో ఈ వ్యాధి అభివృద్ధి చెందుతుంది. అయోడిన్ లోపం ఉన్న ప్రాంతాల్లో పెరుగుతున్న పిల్లలలో కూడా గ్రంథివాపు వ్యాధి సంక్రమిస్తుంది. దీనివల్ల పెరుగుదల ఆలస్యమవడం, శిశువులకు చికిత్స చేయకపోతే మేధో బలహీనత వంటి సమస్యలు వస్తాయి.
వ్యాధి కారణాలు
| సమూహం | కారణాలు |
|---|---|
| ప్రాథమిక హైపోథైరాయిడిజం | బాగా సాధారణమైన విధాలలో హషిమోతో'స్ థైరాయిడిటిస్ (ఒక స్వయం నిరోధిత వ్యాధి), హైపర్ థైరాయిడిజం కొరకు రాడిఅయోడిన్ చికిత్స ఉన్నాయి. |
| సెంట్రల్ హైపోథైరాయిడిజం | పీయూష గ్రంధి, థైరాయిడ్ గ్రంధిని తగినంత థైరాక్సిన్, ట్రైఅయిడోథైరోనిన్ల ఉత్పత్తిని ప్రేరేపించడానికి తగినంత థైరాయిడ్ స్టిమ్యులేటింగ్ హార్మోన్ (TSH) ను ఉత్పత్తి చేయనపుడు సంభవిస్తుంది. ప్రతి ద్వితీయ హైపో థైరాయిడిజానికి నిర్దిష్ట కారణం లేకపోయినప్పటికీ, ఇది సాధారణంగా కణితి, రేడియేషన్ లేదా శస్త్రచికిత్సల వలన పిట్యుటరీ గ్రంధి దెబ్బతిన్నపుడు కలుగుతుంది. |
| పుట్టుకతో వచ్చే హైపోథైరాయిడిజం | హైపోథాలమస్ తగినంత థైరోట్రోపిన్-రెలీసింగ్ హార్మోన్ (TRH) ను ఉత్పత్తి చేసినపుడు సంభవిస్తుంది. TRH పిట్యుటరీ గ్రంధిని థైరాయిడ్ స్టిమ్యులేటింగ్ హార్మోన్ (TSH) ను ఉత్పత్తి చేసేందుకు పురికొల్పుతుంది. అందువలన దీనిని హైపోథాలమిక్-పిట్యుటరి-ఆక్సిస్ హైపో థైరాయిడిజం అని కూడా అనవచ్చు. |

1811లో, బెర్నార్డ్ కోర్టోయిస్ అనే శాస్త్రవేత్త సముద్రపు నాచులో అయోడిన్ ఉందని కనుగొన్నాడు. అయోడిన్ తీసుకోమనేది గ్రంథివ్యాధి పరిమాణంతో ముడిపడి ఉందని 1820లో జీన్-ఫ్రాంకోయిస్ కోయిండెట్ అనే శాస్త్రవేత్త తెలిపాడు. తగినంత అయోడిన్ తీసుకోకపోవడం వల్ల జరిగే అనర్థాలను 1852లో గోయిటర్గ్యాస్పార్డ్ అడాల్ఫ్ చాటిన్ అనే శాస్త్రవేత్త ప్రతిపాదించగా, 1896లో యూజెన్ బామన్ అనే శాస్త్రవేత్త థైరాయిడ్ కణజాలంలో అయోడిన్ను ప్రదర్శించాడు.
మూలాలు
- ↑ "hypothyroidism". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House.
- ↑ "hypothyroidism - definition of hypothyroidism in English from the Oxford dictionary". OxfordDictionaries.com. Retrieved 2016-01-20.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 "Hypothyroidism". National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. March 2013. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Preedy, Victor (2009). Comprehensive Handbook of Iodine Nutritional, Biochemical, Pathological and Therapeutic Aspects. Burlington: Elsevier. p. 616. ISBN 9780080920863.
- ↑ Ferri, Fred F. (2010). Ferri's differential diagnosis : a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders (2nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby. p. Chapter H. ISBN 978-0323076999.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J (2011). "341: disorders of the thyroid gland". Harrison's principles of internal medicine (18th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0071748896.
ఇతర లంకెలు
- "Hypothyroidism information for patients". American Thyroid Association. Retrieved 2017-03-25.
- "UK Guidelines for the use of thyroid function tests" (PDF). The Association for Clinical Biochemistry, British Thyroid Association and British Thyroid Foundation. 2006. Retrieved 2013-12-25.