ట్రైకోమోనాస్: కూర్పుల మధ్య తేడాలు
Rajasekhar1961 (చర్చ | రచనలు) |
Rajasekhar1961 (చర్చ | రచనలు) |
||
| పంక్తి 22: | పంక్తి 22: | ||
[[Image:Pap test trichomonas.JPG|thumb|right|Pap smear, showing infestation by ''Trichomonas vaginalis''. Papanicolau stain, 400x.]] |
[[Image:Pap test trichomonas.JPG|thumb|right|Pap smear, showing infestation by ''Trichomonas vaginalis''. Papanicolau stain, 400x.]] |
||
సామాన్యంగా చేసే [[పాప్ స్మియర్]] పరీక్ష (Pap smear) లో ఇవి కనిపించినా అనుభవం లేనివారికి వీనిని గుర్తించడం కష్టం, అందువలన ఈ పరీక్ష ద్వారా వ్యాధి గుర్తించే వారి సంఖ్య తక్కువగా ఉంటుంది. ట్రైకోమోనాస్ క్రిముల్ని యోనిద్రవాలను తడిగానే సూక్ష్మదర్శిని ద్వారా పరీక్షించి వీనియొక్క స్క్రూ చలనం మూలంగా సులువుగా గుర్తించవచ్చును. ప్రస్తుతం అన్నింటి కన్నా క్రిముల వర్ధనం (Culture) ద్వారా వ్యాధిని నిర్ధారించవచ్చును.<ref name=Ohlermeyer_1998>{{cite journal |author=Ohlemeyer CL, Hornberger LL, Lynch DA, Swierkosz EM |title=Diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis in adolescent females: InPouch TV culture versus wet-mount microscopy |journal=The Journal of adolescent health : official publication of the Society for Adolescent Medicine |volume=22 |issue=3 |pages=205–8 |year=1998 |month=March |pmid=9502007 |doi= |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1054139X97002140}}</ref><ref name=Sood_2007>{{cite journal |author=Sood S, et al |title=InPouch TV culture for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis. |journal=Indian J Med Res |volume=125 |pages=567-571 |pmid=17598943 |year=2007}}</ref> with a sensitivity range of 75-95%.<ref name=pmid17578778>{{cite journal | title=Rapid antigen testing compares favorably with transcription-mediated amplification assay for the detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in young women. | author = Huppert JS | coauthors = Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Miller WC, Hobbs M | journal = Clinical Infectious Diseases | date = July 15 2007 | volume = 45 | issue = 2 | pages = 194-198 | pmid = 17578778 | doi = 10.1086/518851 | url = http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/full/10.1086/518851 |
సామాన్యంగా చేసే [[పాప్ స్మియర్]] పరీక్ష (Pap smear) లో ఇవి కనిపించినా అనుభవం లేనివారికి వీనిని గుర్తించడం కష్టం, అందువలన ఈ పరీక్ష ద్వారా వ్యాధి గుర్తించే వారి సంఖ్య తక్కువగా ఉంటుంది. ట్రైకోమోనాస్ క్రిముల్ని యోనిద్రవాలను తడిగానే సూక్ష్మదర్శిని ద్వారా పరీక్షించి వీనియొక్క స్క్రూ చలనం మూలంగా సులువుగా గుర్తించవచ్చును. ప్రస్తుతం అన్నింటి కన్నా క్రిముల వర్ధనం (Culture) ద్వారా వ్యాధిని నిర్ధారించవచ్చును.<ref name=Ohlermeyer_1998>{{cite journal |author=Ohlemeyer CL, Hornberger LL, Lynch DA, Swierkosz EM |title=Diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis in adolescent females: InPouch TV culture versus wet-mount microscopy |journal=The Journal of adolescent health : official publication of the Society for Adolescent Medicine |volume=22 |issue=3 |pages=205–8 |year=1998 |month=March |pmid=9502007 |doi= |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1054139X97002140}}</ref><ref name=Sood_2007>{{cite journal |author=Sood S, et al |title=InPouch TV culture for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis. |journal=Indian J Med Res |volume=125 |pages=567-571 |pmid=17598943 |year=2007}}</ref> with a sensitivity range of 75-95%.<ref name=pmid17578778>{{cite journal | title=Rapid antigen testing compares favorably with transcription-mediated amplification assay for the detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in young women. | author = Huppert JS | coauthors = Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Miller WC, Hobbs M | journal = Clinical Infectious Diseases | date = July 15 2007 | volume = 45 | issue = 2 | pages = 194-198 | pmid = 17578778 | doi = 10.1086/518851 | url = http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/full/10.1086/518851}}</ref> |
||
ఈ వ్యాధిని మెట్రోనిడజోల్ [[metronidazole]] లేదా టినిడజోల్ [[tinidazole]] మాత్రలతో సులువుగా నయం చేయవచ్చును. should be prescribed to any [[sexual partner]](s) as well because they may potentially be [[asymptomatic carrier]]s.<ref name=Cudmore_2004>{{cite journal |author=Cudmore SL, Delgaty KL, Hayward-McClelland SF, Petrin DP, Garber GE |title=Treatment of infections caused by metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis |journal=Clinical microbiology reviews |volume=17 |issue=4 |pages=783–93, table of contents |year=2004 |month=October |pmid=15489348 |pmc=523556 |doi=10.1128/CMR.17.4.783-793.2004 |url=http://cmr.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15489348}}</ref> |
|||
==మూలాలు== |
==మూలాలు== |
||
14:56, 19 మార్చి 2009 నాటి కూర్పు
| ట్రైకోమోనాస్ వజినాలిస్ | |
|---|---|

| |
| Giemsa-stained culture of T. vaginalis | |
| శాస్త్రీయ వర్గీకరణ | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | టి.వజినాలిస్
|
| Binomial name | |
| ట్రైకోమోనాస్ వజినాలిస్ (Donné 1836)
| |
ట్రైకోమోనాస్ వజినాలిస్ (Trichomonas vaginalis), ప్రోటోజోవా కు చెందిన ఒక పరాన్న జీవి. దీని వలన వచ్చే వ్యాధిని ట్రైకోమోనియాసిస్ (Trichomoniasis) అంటారు. ఇది అభివృద్ధి చెందిన దేశాలలో సంభవించే ప్రోటోజోవా వ్యాధి.[1] ప్రపంచ ఆరోగ్య సంస్థ (WHO) అంచనాల ప్రకారం ప్రపంచవ్యాప్తంగా ప్రతి సంవత్సరం 180 మిలియన్ ప్రజలు దీని బారిన పడుతున్నారు. ఒక్క దక్షిణ అమెరికా లోనే సుమారు 5 నుండి 8 మిలియన్ కొత్త కేసులు గుర్తిస్తున్నారు; అందులో సగం మందికి ఏ విధమైన వ్యాధి లక్షణాలు లేవు.[2]
ట్రైకోమోనియాసిస్
ట్రైకోమోనియాసిస్ (Trichomoniasis) రతి ద్వారా వ్యాపించే అంటు వ్యాధి. ఇది ఎక్కువగా స్త్రీలలో కనిపిస్తుంది. యోని (Vagina) లోని ఆమ్లత్వం తగ్గినప్పుడు ట్రైకోమోనాస్ పెంపొంది వ్యాధిని కలుగజేస్తాయి. ఈ వ్యాధి మూలంగా నెలలు నిండకుండా కాన్పు రావడం, పిల్లలు తక్కువ బరువుండడం జరుగుతుంది.[3] టి.వజినాలిస్ వలన ముత్ర వ్యవస్థ, ఫెలోపియన్ నాళాలు మరియు కటిలో ఇన్ఫెక్షన్ రావచ్చును. సామాన్యంగా ఇది సోకిన స్త్రీలకు పసుపు ఆకుపచ్చని యోని ద్రవాలు ఊరి దురదను కలిగిస్తాయి. తొడుగు (Condom) ఉపయోగించడం వలన దీనినుండి రక్షించుకోవచ్చును.
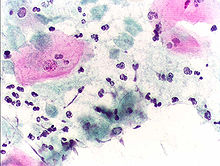
సామాన్యంగా చేసే పాప్ స్మియర్ పరీక్ష (Pap smear) లో ఇవి కనిపించినా అనుభవం లేనివారికి వీనిని గుర్తించడం కష్టం, అందువలన ఈ పరీక్ష ద్వారా వ్యాధి గుర్తించే వారి సంఖ్య తక్కువగా ఉంటుంది. ట్రైకోమోనాస్ క్రిముల్ని యోనిద్రవాలను తడిగానే సూక్ష్మదర్శిని ద్వారా పరీక్షించి వీనియొక్క స్క్రూ చలనం మూలంగా సులువుగా గుర్తించవచ్చును. ప్రస్తుతం అన్నింటి కన్నా క్రిముల వర్ధనం (Culture) ద్వారా వ్యాధిని నిర్ధారించవచ్చును.[4][5] with a sensitivity range of 75-95%.[6]
ఈ వ్యాధిని మెట్రోనిడజోల్ metronidazole లేదా టినిడజోల్ tinidazole మాత్రలతో సులువుగా నయం చేయవచ్చును. should be prescribed to any sexual partner(s) as well because they may potentially be asymptomatic carriers.[7]
మూలాలు
- ↑ Soper D (2004). "Trichomoniasis: under control or undercontrolled?". American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. 190 (1): 281–90. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2003.08.023. PMID 14749674.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Hook EW (1999). "Trichomonas vaginalis--no longer a minor STD". Sexually transmitted diseases. 26 (7): 388–9. PMID 10458631.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Schwebke JR, Burgess D (2004). "Trichomoniasis". Clinical microbiology reviews. 17 (4): 794–803, table of contents. doi:10.1128/CMR.17.4.794-803.2004. PMC 523559. PMID 15489349.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Ohlemeyer CL, Hornberger LL, Lynch DA, Swierkosz EM (1998). "Diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis in adolescent females: InPouch TV culture versus wet-mount microscopy". The Journal of adolescent health : official publication of the Society for Adolescent Medicine. 22 (3): 205–8. PMID 9502007.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Sood S; et al. (2007). "InPouch TV culture for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis". Indian J Med Res. 125: 567–571. PMID 17598943.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ↑ Huppert JS (July 15 2007). "Rapid antigen testing compares favorably with transcription-mediated amplification assay for the detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in young women". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 45 (2): 194–198. doi:10.1086/518851. PMID 17578778.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ Cudmore SL, Delgaty KL, Hayward-McClelland SF, Petrin DP, Garber GE (2004). "Treatment of infections caused by metronidazole-resistant Trichomonas vaginalis". Clinical microbiology reviews. 17 (4): 783–93, table of contents. doi:10.1128/CMR.17.4.783-793.2004. PMC 523556. PMID 15489348.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)