ఎస్టర్
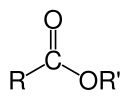
ఎస్టర్లు (Esters) ఆమ్లాలు ఆల్కహాల్ లేదాఫినాల్తో చర్య జరపడం వలన తయారయే రసాయన పదార్ధాలు.[1] ఇవి సామాన్యంగా అకార్బనిక లేదా కార్బనిక అమ్లాల నుండి వస్తాయి.
ఎస్టర్లు విశ్వవ్యాప్తంగా కనిపిస్తాయి. ప్రకృతిలో చాలా నూనెలు, కొవ్వులలో గ్లిజరాల్ ఎస్టర్లుగా ఉంటాయి. తక్కువ అణు భారం కలిగిన ఎస్టర్లు సుగంధ ద్రవ్యాలుగా ఉపయోగిస్తారు. ఫాస్ఫేట్ ఎస్టర్లు డి.ఎన్.ఎ.లో ముఖ్యమైన భాగం. నైట్రోగ్లిసరిన్ (Nitroglycerin) నైట్రేట్ ఎస్టర్లు ప్రధానమైన ప్రేలుడు పదార్ధాలు. ప్లాస్టిక్లో అతి ముఖ్యమైనది పోలీఎస్టర్లు.
ఎస్టర్ అనే పదాన్ని మొదటిసారి జర్మనీ రసాయనిక శాస్త్రవేత్త లియోపోల్డ్ మెలిన్ (Leopold Gmelin) 1848లో ఉపయోగించారు.[2]
మూలాలు
[మార్చు]- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "esters".
- ↑ Leopold Gmelin, Handbuch der Chemie, vol. 4: Handbuch der organischen Chemie (vol. 1) (Heidelberg, Baden (Germany): Karl Winter, 1848), page 182.
Original text:
Translation:b. Ester oder sauerstoffsäure Aetherarten.
Ethers du troisième genre.
Viele mineralische und organische Sauerstoffsäuren treten mit einer Alkohol-Art unter Ausscheidung von Wasser zu neutralen flüchtigen ätherischen Verbindungen zusammen, welche man als gepaarte Verbindungen von Alkohol und Säuren-Wasser oder, nach der Radicaltheorie, als Salze betrachten kann, in welchen eine Säure mit einem Aether verbunden ist.b. Ester or oxy-acid ethers.
Ethers of the third type.
Many mineral and organic acids containing oxygen combine with an alcohol upon elimination of water to [form] neutral, volatile ether compounds, which one can view as coupled compounds of alcohol and acid-water, or, according to the theory of radicals, as salts in which an acid is bonded with an ether.
