ఫారెన్హీట్

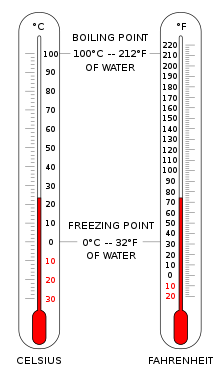
ఫారెన్హీట్ అనేది జర్మన్ భౌతిక శాస్త్రవేత్త డేనియల్ గాబ్రియల్ ఫారెన్హీట్ (1686-1736) ద్వారా 1724 లో ప్రతిపాదించిన ఒక ఆధారంగా ఉష్ణోగ్రత స్కేలు, తర్వాత ఈ స్కేలుకు ఇతని పేరు పెట్టారు.[1] దీని యూనిట్ గా డిగ్రీ ఫారన్హీట్ (చిహ్నం °F) ఉపయోగిస్తారు. దీని తక్కువ నిర్వచన పాయింట్ 0 డిగ్రీలు, మంచు, ఉప్పు సమాన భాగాల నుంచి తయారయ్యే ఉప్పునీరు యొక్క ఒక పరిష్కారం యొక్క ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద స్థిర పరచబడింది. మరిన్ని పరిమితులుగా మంచు యొక్క కరిగే స్థానం 32 డిగ్రీలు గా, తన ఉత్తమ అంచనాగా సగటు మానవ శరీర ఉష్ణోగ్రత 96 డిగ్రీలు (ఆధునిక కొలత కంటే 2.5 డిగ్రీలు తక్కువ) గా ప్రతిపాదించబడ్డాయి.[2] ఈ స్కేలు ఇప్పుడు సాధారణంగా రెండు స్థిర బిందువులచే నిర్వచించబడింది:నీరు మంచుగా గడ్డకట్టే 32 డిగ్రీల వద్ద, నీరు మరిగే 212 డిగ్రీలు. By the end of the 20th century, Fahrenheit was only used as the official temperature scale in the United States, the Bahamas, Belize, the Cayman Islands, and Palau. All other countries in the world now use the Celsius scale, defined since 1954 by absolute zero being −273.15 °C and the triple point of water being at 0.01 °C.[3] However, the Fahrenheit scale remains in common unofficial use in many of the current and former US unincorporated territories.

మూలాలు
[మార్చు]- ↑ Robert T. Balmer (2010). Modern Engineering Thermodynamics. Academic Press. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-12-374996-3. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ↑ Fahrenheit temperature scale, Encyclopedia Britannica Onlinbe. 25 September 2015
- ↑ Celsius vs. Fahrenheit
