గాంబియా: కూర్పుల మధ్య తేడాలు
| పంక్తి 160: | పంక్తి 160: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
</ref> |
</ref> |
||
==Economy== |
|||
[[File:2014 Gambia Products Export Treemap.png|thumb|Gambia Exports by Product (2014) from [http://atlas.cid.harvard.edu/explore/tree_map/export/gmb/all/show/2014/ Harvard Atlas of Economic Complexity] ]] |
|||
{{Main|Economy of the Gambia}} |
|||
[[File:People tourists in swimming pool hotel Gambia.jpg|thumb|Tourists in Gambia, 2014]] |
|||
The Gambia has a liberal, [[Market economy|market-based economy]] characterised by traditional subsistence agriculture, a historic reliance on groundnuts (peanuts) for export earnings, a re-export trade built up around its ocean port, low import duties, minimal administrative procedures, a fluctuating exchange rate with no exchange controls, and a significant tourism industry.<ref name="bn"/> |
|||
The World Bank pegged Gambian GDP for 2011 at US$898M; the International Monetary Fund put it at US$977M for 2011. |
|||
From 2006 to 2012, the Gambian economy grew annually at a pace of 5–6% of GDP.<ref>Fadera, Hatab (23 April 2012) [https://web.archive.org/web/20141129035755/http://observer.gm/africa/gambia/article/gambia-to-commence-rail-system-in-2013-discloses-president-jammeh-as-he-opens-parliament "Gambia to commence rail system in 2013:- Discloses President Jammeh, as he opens parliament"], ''The Daily Observer'' (23 April 2012).</ref> |
|||
Agriculture accounts for roughly 30% of gross domestic product (GDP) and employs about 70% of the labour force. Within agriculture, peanut production accounts for 6.9% of GDP, other crops 8.3%, livestock 5.3%, fishing 1.8%, and forestry 0.5%. Industry accounts for about 8% of GDP and services around 58%. The limited amount of manufacturing is primarily agricultural-based (e.g., peanut processing, bakeries, a brewery, and a tannery). Other manufacturing activities include soap, [[soft drinks]], and clothing.<ref name="bn"/> |
|||
Previously, the United Kingdom and other EU countries constituted the major Gambian export markets. However, in recent years Senegal, the United States, and Japan have become significant trade partners of the Gambia. In Africa, Senegal represented the biggest trade partner of the Gambia in 2007, which is a defining contrast to previous years that had Guinea-Bissau and Ghana as equally important trade partners. Globally, Denmark, the United States, and China have become important source countries for Gambian imports. The UK, Germany, [[Ivory Coast]], and the Netherlands also provide a fair share of Gambian imports. The Gambian trade deficit for 2007 was $331 million.<ref name="bn"/> |
|||
In May 2009, 12 commercial banks existed in the Gambia, including one Islamic bank. The oldest of these, [[Standard Chartered Bank]], dates its presence back to the entry in 1894 of what shortly thereafter became [[Bank of British West Africa]]. In 2005, the Swiss-based banking group International Commercial Bank established a subsidiary and now has four branches in the country. In 2007, Nigeria's [[Access Bank plc|Access Bank]] established a subsidiary that now has four branches in the country, in addition to its head office; the bank has pledged to open four more. |
|||
In May 2009, the Lebanese Canadian Bank opened a subsidiary called [[Prime Bank (Gambia)|Prime Bank]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://observer.gm/africa/gambia/article/another-new-bank-inaugurated |title=Prime Bank (Gambia) is the 12th commercial bank in the Gambia |publisher=Observer.gm |date=27 May 2009 |accessdate=26 June 2010 |deadurl=bot: unknown |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140719122332/http://observer.gm/africa/gambia/article/another-new-bank-inaugurated |archivedate=19 July 2014 |df= }}</ref> |
|||
<gallery widths="250" heights="170"> |
|||
Serekunda market.jpg|[[Serekunda]] market |
|||
Fishing boat The Gambia.jpg|Brightly-painted fishing boats are common in [[Bakau]] |
|||
Green monkey (Chlorocebus sabaeus) juvenile head.jpg|The Gambia's wildlife, like this [[green monkey]], attracts tourists |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== బయటి లింకులు == |
== బయటి లింకులు == |
||
05:49, 5 మార్చి 2019 నాటి కూర్పు
రిపబ్లిక్ ఆఫ్ ది గాంబియా |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| నినాదం "Progress, Peace, Prosperity" |
||||
| జాతీయగీతం For The Gambia Our Homeland |
||||
 |
||||
| రాజధాని | బంజుల్ 13°28′N 16°36′W / 13.467°N 16.600°W | |||
| అతి పెద్ద నగరం | సెర్రెకుండ | |||
| అధికార భాషలు | ఆంగ్లం | |||
| ప్రజానామము | గాంబియన్ | |||
| ప్రభుత్వం | రిపబ్లిక్కు | |||
| - | President | Yahya A.J.J. Jammeh[1] | ||
| Independence | ||||
| - | from the UK | February 18 1965 | ||
| - | Republic declared | April 24 1970 | ||
| - | జలాలు (%) | 11.5 | ||
| జనాభా | ||||
| - | 2007 United Nation అంచనా | 1,700,000 (146వది) | ||
| జీడీపీ (PPP) | 2008 అంచనా | |||
| - | మొత్తం | $2.264 billion[2] | ||
| - | తలసరి | $1,389[2] | ||
| జీడీపీ (nominal) | 2008 అంచనా | |||
| - | మొత్తం | $808 million[2] | ||
| - | తలసరి | $495[2] | ||
| జినీ? (1998) | 50.2 (high) | |||
| మా.సూ (హెచ్.డి.ఐ) (2006) | ||||
| కరెన్సీ | Dalasi (GMD) |
|||
| కాలాంశం | GMT | |||
| ఇంటర్నెట్ డొమైన్ కోడ్ | .gm | |||
| కాలింగ్ కోడ్ | +220 | |||
గాంబియా (ఆంగ్లం : The Gambia) [3] అధికారిక నామం "రిపబ్లిక్ ఆఫ్ ద గాంబియా", సాధారణంగా గాంబియా అని పిలువబడుతుంది. పశ్చిమ ఆఫ్రికా లోని ఒక దేశం. ప్రధాన ఆఫ్రికాలోని ఒక చిన్న దేశం. ఈ దేశం చుట్టూ ఉత్తరాన, తూర్పున మరియు దక్షిణాన సెనెగల్ వ్యాపించి యున్నది. దేశ పశ్చిమతీరంలో అట్లాంటిక్ మహాసముద్రం ఉంది. దీని రాజధాని బంజుల్.[4]
గాంబియా దేశం గాంబియా నదికి ఇరువైపులా ఉంది. గాంబియా నది దేశం మద్యలో ప్రవహించి అట్లాంటికు మహాసముద్రంలోకి సంగమిస్తుంది. 2013 ఏప్రెలు గణాంకాల ఆధారంగా దేశజనసంఖ్య 18,57,181, వైశాల్యం 10,689 చదరపు కిలోమీటర్లు (4,127 చ.మై) ఉంది. బంజులు గాంబియా రాజధానిగా ఉంది. సెరెకుండా, బ్రికమా అతిపెద్ద నగరాలుగా ఉన్నాయి.
గంబియా అనేక ఇతర పశ్చిమ ఆఫ్రికా దేశాలలాగా బానిసవాణిజ్య చారిత్రక మూలాలను కలిగి ఉంది. మొదటగా పోర్చుగీసు వారు గాంబియా నదీతీరంలో ఒక కాలనీని స్థాపించడానికి ఈ ప్రాంతం కీలక అంశంగా ఉంది. పోర్చుగీసువారు ఈ ప్రాంతానికి గాంబియా అని నామకరణం చేసారు. 1765 మే 25 న [5] గాంబియా బ్రిటీషు ప్రభుత్వం అధికారికంగా నియంత్రణను తీసుకున్న తరువాత గాంబియా సామ్రాజ్యంలో భాగంగా మారింది. తరువాత బ్రిటిషు సెనెగాంబియా స్థావరాన్ని స్థాపించింది. 1965 లో గాంబియాకు " దాదా జవరా " నాయకత్వంలో స్వాతంత్ర్యం పొందింది. 1994 లో యహ్యా జమ్మే అధికారాన్ని స్వాధీనం చేసుకుని అధికారాన్ని హస్థగతం చేసుకుని దాదా జవరాను అధికారం నుండి తొలగించారు. 2016 డిసెంబరు ఎన్నికలలో జమ్మేను ఓడించిన అదామా బారో జనవరి 2017 లో గాంబియా మూడవ అధ్యక్షుడు అయ్యాడు.[6] జమ్మీ మొదట ఫలితాలను అంగీకరించి తరువాత నిరాకరించాడు. ఇది గాంబియాలో రాజ్యాంగ సంక్షోభం తలెత్తడానికి కారణం అయింది. పశ్చిమ ఆఫ్రికా దేశాల ఆర్థిక సమాజం సైనిక జోక్యం ఆయన బహిష్కరణకు దారితీసింది.[7][8][9] గాంబియా ఆర్ధికవ్యవస్థ వ్యవసాయం, చేపలు పట్టడం, ముఖ్యంగా, పర్యాటక రంగం మీద ఆధారితమై ఉంది. 2015 లో జనాభాలో 48.6% పేదరికంలో నివసించారు.[10] గ్రామీణ ప్రాంతాల్లో పేదప్రజలు మరింత అధికంగా ఉన్నారు. గ్రామాలలో జనాభాలో అత్యధికంగా పేదలు (దాదాపు 70%) ఉన్నారు.[10]
చరిత్ర
అరబు వర్తకులు 9-10 వ శతాబ్దాలలో గాంబియా ప్రాంతపు మొట్టమొదటి లిఖిత రూప ఆధారాలు అందించారు. 17 వ శతాబ్దంలో ముస్లిం వర్తకులు, పండితులు అనేక పశ్చిమ ఆఫ్రికా వ్యాపార కేంద్రాలలో కమ్యూనిటీలను స్థాపించారు. రెండు సమూహాలు ట్రాన్స్-సహారా వర్తక మార్గాలు స్థాపించాయి. ఈ మార్గాలు బానిసలుగా మార్చబడిన స్థానిక ప్రజలను, బంగారం, దంతాలు ఎగుమతి చేయడానికి, తయారు చేసిన వస్తువుల దిగుమతి వంటి పెద్ద వాణిజ్యానికి దారి తీసింది.

11 వ నుండి 12 వ శతాబ్దినాటికి ఉత్తరప్రాంతంలో సెనెగలు నదితీరంలో కేంద్రీకృతమై ఉన్న తాక్రూరు రాజ్యాల పాలకులు, పురాతన ఘనా, గావో ఇస్లాం మతంలోకి మారిపోయారు. అరబు భాషాప్రావీణ్యం ఉన్న వారిని రాజ్యసభలో ఉద్యోగులుగా నియమించారు.[11] 14 వ శతాబ్దం ప్రారంభంలో ప్రస్తుత గాంబియాలో చాలా భాగం మాలి సామ్రాజ్యంలో భాగంగా ఉందేది. 15 వ శతాబ్దం మధ్యకాలంలో పోర్చుగీసు అన్వేషకులు సముద్రం మార్గంలో ఈ ప్రాంతానికి చేరుకున్న తరువాత విదేశీ వర్తకుల ఆధిపత్యం ప్రారంభం అయింది.
1588 లో పోర్చుగీసు ఆంటోనియోకు గాంబియా నదిమీద ప్రత్యేక వాణిజ్య హక్కులను ఇంగ్లీషు వ్యాపారులకు విక్రయించింది. మొదటి ఎలిజబెతు రాణి పేటెంటు లేఖలను మంజూరు చేసింది. 1618 లో ఇంగ్లాండు రాజు మొదటి జేమ్సు గాంబియా గోల్డ్ కోస్టు (ప్రస్తుతం ఘనా) తో వాణిజ్యానికి ఒక ఆంగ్ల కంపెనీకి ఒక చార్టర్ను మంజూరు చేసాడు. 1651 - 1661 మధ్యకాలంలో డచీ ఆఫ్ కోర్లాండు, సెమిగాలియా పాలనలో పోలిష్-లిథువేనియన్ కామన్వెల్త్-ఆధునిక లాట్వియా నియంత్రణలో ఉన్న గాంబియా లోని కొన్ని భాగాలు ప్రిన్సు జాకబు కెట్లర్బు చేత కొనుగోలు చేయబడ్డాయి.[12].
17 వ శతాబ్దం చివర నుండి 18 వ శతాబ్దం వరకు సెనెగలు నది, గాంబియా ప్రాంతాలలో రాజకీయ, వాణిజ్య ఆధిపత్యం కోసం బ్రిటీషు సామ్రాజ్యం, ఫ్రెంచి సామ్రాజ్యం నిరంతరంగా పోరాడాయి. 1758 లో సెనెగలు ఆక్రమణ తరువాత అగస్టసు కెప్పెలు నేతృత్వంలో జరిగిన ఒక దండయాత్ర ద్వారా బ్రిటిషు సామ్రాజ్యం గాంబియాను ఆక్రమించింది. 1783 లో వెర్సైల్లెసు ఒప్పందంతో గ్రేట్ బ్రిటన్ గాంబియా నదీప్రాంతాన్ని స్వాధీనం చేసుకుంది. ఫ్రెంచి నది అల్బ్రేడా వద్ద ఒక చిన్న ప్రదేశం నిలుపుకుంది. ఉత్తర తీరం 1856 చివరినాటికి యునైటెడు కింగ్డంకు ఇవ్వబడింది.
మూడు శతాబ్దాల కాలంలో ట్రాంసు అట్లాంటికు వాణిజ్యంలో భాగంగా ఈ ప్రాంతంలోని మూడు మిలియన్ల మంది బానిసలుగా తీసుకునివెళ్ళబడ్డారు. అట్లాంటికు బానిస వాణిజ్యం ప్రారంభమవడానికి ముందు గిరిజన యుద్ధాలు కారణంగా, ముస్లిం వర్తకుల వాణిజ్యంలో ఎంతమంది బానిసలుగా మార్చబడ్డారో ఖచ్ఛితమైన వివరణ లేదు. వారిలో చాలా మంది ఇతర ఆఫ్రికన్లను ఐరోపావాసులకు విక్రయించారు. కొంతమంది గిరిజనుల అంతర్యుద్ధ ఖైదీలుగా ఉన్నారు. చెల్లించని రుణాల కారణంగా కొన్ని బాధితులను బానిసలుగా అమ్ముతారు. చాలామంది ఇతరులు అపహరణకు గురై బానిసలుగా విక్రయించబడ్డారు.[13]
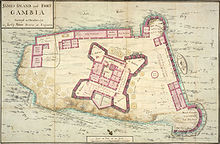
18 వ శతాబ్దంలో వెస్ట్ ఇండీసు, ఉత్తర అమెరికాలో కార్మిక మార్కెట్టు విస్తరణ వరకు వ్యాపారులు మొదట ప్రజలను ఐరోపాకు పంపారు. 1807 లో యునైటెడ్ కింగ్డం దాని సామ్రాజ్యం అంతటా బానిస వాణిజ్యాన్ని రద్దు చేసింది. తరువాత గాంబియాలో బానిస వ్యాపారాన్ని అంతం చేయడానికి విఫల ప్రయత్నం చేసింది. బానిస నౌకలను రాయలు నేవీకి చెందిన " పశ్చిమ ఆఫ్రికన్ స్క్వాడ్రన్ " చేత అడ్డగించబడిన బానిస నౌకలు గాంబియాకు తిరిగి వచ్చాయి. గాంబియా నదికి సమీపంలో ఉన్న మాకర్తి ద్వీపంలో విడువబడిన బానిసలు వారు కొత్త జీవితాలను ప్రారంభించాలని భావించారు.[14] 1816 లో బ్రిటిషు బాతుర్స్టు (ప్రస్తుతం బంజులు)ప్రాంతంలో సైనిక శిబిరాన్ని ఏర్పాటు చేసింది.
గాంబియా కాలనీ మరియు ప్రొటెక్టరేటు (1821–1965)

తరువాతి సంవత్సరాలలో కొన్నిమార్లు బంజులు సియర్రా లియోనిలోని బ్రిటీషు గవర్నరు-జనరలు అధికార పరిధిలో ఉంది. 1888 లో గాంబియా ఒక ప్రత్యేక కాలనీగా మారింది.
1889 లో బ్రిటిషు ఫ్రెంచి రిపబ్లికుతో ఒక ఒప్పందం తరువాత ప్రస్తుత సరిహద్దులను స్థాపించింది. తరువాత గాంబియా బ్రిటీషు గాంబియా అని పిలిచే బ్రిటీషు క్రౌను కాలనీగా మారింది. ఇది పరిపాలనా సౌలభ్యం కొరకు కాలనీ (బంజులు చుట్టుపక్కల ప్రాంతం), సంరక్షక (పరిపాలనా ప్రాంతం) ప్రాంతాలుగా విభజించబడింది. 1901 లో గాంబియాకు దాని స్వంత ఎగ్జిక్యూటివ్ శాసన కౌన్సిలు మంజూరు చేయబడింది. ఇది క్రమంగా స్వీయ-ప్రభుత్వానికి దారితీసింది. 1906 లో బానిసత్వం నిషేధించబడింది. బ్రిటీషు వలసరాజ్య శక్తులు స్వదేశీ గాంబియన్ల మధ్య ఒక చిన్న సంఘర్షణ తరువాత బ్రిటీషు వలసరాజ్య అధికారం నిలకడగా స్థాపించబడింది.[15]
రెండో ప్రపంచ యుద్ధం సమయంలో కొంతమంది సైనికులు మిత్రరాజ్యాలతో పోరాడారు. ఈ సైనికులు ఎక్కువగా బర్మాలో పోరాడినప్పటికీ కొందరు ఇంటికి చేరిన తరువాత మరణించారు. వీరికి ఫజరాలో " కామన్వెల్త్ వార్ గ్రేవ్స్ కమీషన్ " స్మశానం (బంజులుకు సమీపంలో) ఉంది. బంజులులో " యు.ఎస్. ఆర్మీ ఎయిర్ ఫోర్సెసు " ఎయిర్ స్ట్రిపు ఉంది. ఇక్కడి నౌకాశ్రయంలో మిత్రరాజ్య నౌకాదళ నౌకలు నిలుపబడ్డాయి.
రెండవ ప్రపంచ యుద్ధం తరువాత రాజ్యాంగ సంస్కరణల వేగం అధికరించింది. 1962 లో సాధారణ ఎన్నికలను తరువాత సంవత్సరంలో యునైటెడు కింగ్డం పూర్తి అంతర్గత స్వీయ-పాలనను మంజూరు చేసింది.

స్వతంత్రం తరువాత (1965–ప్రస్తుతం)
1965 ఫిబ్రవరి 18 న కామన్వెల్తులో భాగంగా రెండవ ఎలిజబెతురాణిని గాంబియా రాణిగా అంగీకరిస్తూ రూపొందించబడిన గాంబియా రాచరిక రాజ్యానికి గవర్నరు ప్రాతినిధ్యం వహించాడు. తరువాత కొంతకాలానికి జాతీయ ప్రభుత్వం గాంబియా రిపబ్లికుగా ప్రతిపాదిస్తూ ప్రజాభిప్రాయ సేకరణను నిర్వహించింది. రాజ్యాంగంను సవరించడానికి అవసరమైన మూడింట రెండు వంతుల మెజారిటీని సాధించడంలో ఈ ప్రజాభిప్రాయసేకరణ విఫలమైంది. కాని ఫలితాలు విదేశాల పరిశీలకుల దృష్టిని విస్తృతంగా ఆకర్షించింది.[ఆధారం చూపాలి]
1970 ఏప్రెలు 24 న రెండవ ప్రజాభిప్రాయ సేకరణ తరువాత గాంబియా కామన్వెల్తులో గణతంత్ర రాజ్యంగా మారింది. ప్రధానిగా సర్ దాదా కైరాబా జవరా అధ్యక్షుడి కార్యదర్శిగా బాధ్యతలు స్వీకరించారు.
అధ్యక్షుడుగా సర్ దాదా జవరా తిరిగి ఐదుసార్లు ఎన్నికయ్యారు. 1981 జూలై 29 న జరిగిన ఒక తిరుగుబాటు తరువాత ఆర్ధికరంగం బలహీనపడి రాజకీయవేత్తలకు వ్యతిరేకంగా అవినీతి ఆరోపణలు చేయబడ్డాయి.[16]అధ్యక్షుడు జవరా లండనును సందర్శించిన సమయంలో సోషలిస్టు కుకొయి సాంబా సన్యంగు వ్యూహంలో వామపక్ష " నేషనల్ రివల్యూషనరీ కౌంసిల్ ", రివల్యూషనరీ సోషలిస్టు పార్టీ కౌంస్లిలు, దేశ సైనికదళాలు అధ్యక్షుడికి వ్యతిరేకంగా తిరుగుబాటు చేసారు. [16]
అధ్యక్షుడు జవరా సెనెగలు నుండి సైనిక సాయం కోరాడు. జులై 31 న గాంబియాకు 400 మంది సైనికులను నియమించారు. ఆగస్టు 6 నాటికి, 2,700 సెనెగలు సైనికులు తిరుగుబాటు బలగాలను ఓడించారు.[16] తిరుగుబాటు సమయంలో, తరువాత జరిగిన హింసాకాండలో 500 - 800 మంది చంపబడ్డారు.[16] 1981 లో జరిగిన తిరుగుబాటు తరువాత 1982 లో సెనెగలు, గాంబియా సమాఖ్య ఒప్పందంలో సంతకం చేశాయి. సెనెగాంబియా కాన్ఫెడరేషన్ రెండు దేశాల సాయుధ దళాలను మిళితం చేసి వారి ఆర్థిక వ్యవస్థలు, కరెన్సీలను ఏకం చేయాలని లక్ష్యంగా పెట్టుకుంది. కేవలం ఏడు సంవత్సరాల తర్వాత 1989 లో కాంఫిడరేషను నుండి గాంబియా శాశ్వతంగా నిష్క్రమించింది.
1994 లో సాయుధ దళాల తాత్కాలిక పాలనా మండలి జవరా ప్రభుత్వాన్ని తొలగించి ప్రతిపక్ష రాజకీయ కార్యకలాపాలను నిషేధించింది. లెఫ్టినెంటు యాహ్యా ఎ.జె.జె. జమ్మీ, ఎ.ఎఫ్.పి.ఆర్.సి. చైర్మను దేశ అధిపతి అయ్యాడు. తిరుగుబాటు సమయంలో జమ్మీ వయసు కేవలం 29 సంవత్సరాలు మాత్రమే. ఎ.ఎఫ్.పి.ఆర్.సి. ప్రజాస్వామ్య ప్రభుత్వానికి తిరిగి రావడానికి ప్రణాళికను ప్రకటించింది. 1996 లో ఓటర్లు నమోదు చేయడానికి, ఎన్నికలు, ప్రజాభిప్రాయ నిర్వహణకు ఇండిపెండెంట్ ఎలక్టోరల్ కమిషన్ (ఐ.ఇ.సి.) స్థాపించబడింది.
2001 చివరలో, 2002 ఆరంభంలో గాంబియా అధ్యక్ష శాసన, స్థానిక ఎన్నికల పూర్తి చక్రం పూర్తి చేసింది. విదేశీ పరిశీలకులు ఎన్నికలను స్వేచ్ఛ, న్యాయం, పారదర్శకంగా భావించినప్పటికీ, కొన్ని [లోపాలు] లోపాలు ఉన్నాయని ఉన్నారు. అధ్యక్షుడు యాహ్యా జమ్మెహు తిరుగుబాటును అధిగమించి అధ్యక్షునిగా ఎన్నికై పదవిగా కొనసాగాడు. 2001 డిసెంబరు 21 న తిరిగి బాధ్యతలు స్వీకరించారు. జాతీయ అసెంబ్లీలో జమ్మీ " అలయన్సు పేట్రియాటికు రియోరియంటేషను అండ్ కంస్ట్రక్షన్ " (ఎ.పి.ఆర్.సి) తన బలమైన మెజారిటీ ప్రధాన ప్రతిపక్షం యునైటెడ్ డెమోక్రాటిక్ పార్టీ (UDP) శాసన ఎన్నికలను బహిష్కరించిన తరువాత కూడా బలమైన ఆధిఖ్యతను నిలుపుకుంది.
[1]
2013 అక్టోబరు 2 న గాంబియా అంతర్గత వ్యవహారాల మంత్రి గాంబియా కామన్వెల్తును తక్షణమే వదిలిపెడుతుందని ప్రకటించడంతో సంస్థ 48 సంవత్సరాల సభ్యత్వం ముగిసింది. " గాంబియా ఎటువంటి నియో-కాలనీయల్ సంస్థ సభ్యదేశంగా ఉండదని, వలసవాదం విస్తరణకు ప్రాతినిధ్యం వహించే సంస్థలో ఎప్పటికీ భాగస్వామ్యం వహించదని " అని గాంబియా ప్రభుత్వం పేర్కొంది.[17]
అధ్యక్షుడు జమ్మేషు ప్రతిపక్ష నాయకుడు అదమ బారో (ఇండిపెండెంటు కోయిలేషన్ ఆఫ్ పార్టీలు)[18] మమ్మ కండేహ్ (గాంబియా డెమొక్రటిక్ కోయిలేషన్ పార్టీలు),[19] నుండి వ్యతిరేకతను ఎదుర్కొన్నాడు. గాంబియా జులై 2016 జూలైలో ప్రధాన ప్రతిపక్ష నేత, మానవ హక్కుల న్యాయవాది ఔసైనౌ దర్బాయుకు 3 సంవత్సరాల జైలు శిక్ష విధించి[20] అధ్యక్ష ఎన్నికలో పోటీ చేయడానికి ఆయనను అనర్హులుగా ప్రకటించారు.
డిసెంబరు 1 ఎన్నిక తరువాత ఎన్నికల సంఘం అధ్యక్ష ఎన్నికల విజేతగా అడామా బారోను ప్రకటించింది.[21] 22 సంవత్సరాలుగా పాలించిన జమ్మీ 2016 ఎన్నికలలో ఓటమి పొంది ముందుగా పదవి నుండి వైతొలుగుతానని ప్రకటించి ఫలితాలు ప్రకటించడానికి ముందుగా కొత్తగా ఎన్నికలు నిర్వహించడానికి పిలుపు ఇవ్వడంతో ఒక రాజ్యాంగ సంక్షోభానికి కారణమై " ఎకనమిక్ కమ్యూనిటీ ఆఫ్ వెస్టు ఆఫ్రికన్ స్టేట్సు " దాడికి దారితీసింది.[22] 2017 జనవరి 20 న జామ్హె పదవీవిరమణ అంగీకరించి దేశం విడిచిపెడతానని ప్రకటించాడు.[8]
2017 ఫిబ్రవరి 14 న గాంబియా కామన్వెల్తు సభ్యత్వానికి తిరిగి అంగీకరించింది. 2018 జనవరి 22 న తిరిగి కామంవెల్తులో చేరడానికి కార్యదర్శి జనరల్ ప్యాట్రిసియా స్కాట్లాండ్కు తన దరఖాస్తును అధికారికంగా సమర్పించింది.[23][24] 1965 లో దేశం స్వాతంత్ర్యం పొందిన తరువాత గాంబియాను సందర్శించటానికి మొట్టమొదటి బ్రిటీషు విదేశాంగ కార్యదర్శి బోరిసు జాన్సను[25] బ్రిటీషు ప్రభుత్వం కామన్వెల్తుకు గాంబియా తిరిగి వచ్చిందని ప్రకటించాడు.[25]2018 ఫిబ్రవరి 8 న గాంబియా అధికారికంగా తిరిగి కామంవెల్తులో చేరింది.[26][27]
భౌగోళికం


గాంబియా చాలా చిన్న, ఇరుకైన దేశం. దీని సరిహద్దులు గాంబియా నదిని ప్రతిబింబిస్తాయి. ఇది 13 నుండి 14 ° ఉత్తర అక్షాంశం, 13 నుండి 17 ° పశ్చిమ రేఖంశాల పొడవుల మధ్య ఉంటుంది.
గాంబియా 50 కిలోమీటర్లు (31 మైళ్ళు) వెడల్పు ఉంటుంది. దేశవైశాల్యం 11,295 చ.కి.మీ 2 (4,361 చ.కి.మీ). గాంబియా 1,300 చదరపు కి (1.4 × 1010 చదరపు అడుగులు) (11.5%) జలభాగం కలిగి ఉంది. ఇది ఆఫ్రికా ప్రధాన భూభాగంలో అతిచిన్న దేశం. గాంబియా జమైకా ద్వీపం కంటే కొంచెం తక్కువగా ఉంది.
గాంబియా మూడు వైపులా సెనెగలు ఆక్రమించి ఉంటుంది. దేశపశ్చిమ సరిహద్దులో 80 కిలోమీటర్ల (50 మైళ్ళు) పొడవున అట్లాంటిక్ మహాసముద్రతీరం ఉంటుంది.[28]
1889 లో యునైటెడ్ కింగ్డం, ఫ్రాన్సు మధ్య జరిగిన ఒప్పందం తరువాత ప్రస్తుత సరిహద్దులు నిర్ణయించబడింది. పారిసులో ఫ్రెంచి, బ్రిటిషు మధ్య చర్చల సందర్భంగా ఫ్రెంచి గాంబియా నదికి 200 మైళ్ల దూరంలో (320 కిలోమీటర్లు) భూభాగం మీద నియంత్రణను బ్రిటిషుకు స్వాధీనం చేసింది. 1891 లో సరిహద్దులను గుర్తించడంతో ఉంచడంతో ప్రారంభించి దాదాపు 15 సంవత్సరాల తరువాత పారిసు సమావేశాలు నిర్వహించి గాంబియా చివరి సరిహద్దులను నిర్ణయించబడ్డాయి. ఫలితంగా గాంబియా నదికి ఉత్తరం, దక్షిణాన 10 మైళ్ళ (16 కి.మీ.) ప్రాంతం బ్రిటీషు నియంత్రణలోకి ఇవ్వబడింది.[29]
వాతావరణం
గాంబియా ఉష్ణమండల వాతావరణం ఉంటుంది. జూన్ నుండి నవంబరు వరకు వర్షాకాలం కొనసాగుతుంది. నవంబరు నుండి మే వరకు, చల్లటి ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు ఆధిఖ్యత చేస్తుంటాయి.[28]గాంబియాలో వాతావరణం పొరుగున ఉన్న సెనెగలు దక్షిణ మాలి, బెనిన్ ఉత్తర భాగాన్ని పోలి ఉంటుంది.[30]
Economy


The Gambia has a liberal, market-based economy characterised by traditional subsistence agriculture, a historic reliance on groundnuts (peanuts) for export earnings, a re-export trade built up around its ocean port, low import duties, minimal administrative procedures, a fluctuating exchange rate with no exchange controls, and a significant tourism industry.[31]
The World Bank pegged Gambian GDP for 2011 at US$898M; the International Monetary Fund put it at US$977M for 2011.
From 2006 to 2012, the Gambian economy grew annually at a pace of 5–6% of GDP.[32]
Agriculture accounts for roughly 30% of gross domestic product (GDP) and employs about 70% of the labour force. Within agriculture, peanut production accounts for 6.9% of GDP, other crops 8.3%, livestock 5.3%, fishing 1.8%, and forestry 0.5%. Industry accounts for about 8% of GDP and services around 58%. The limited amount of manufacturing is primarily agricultural-based (e.g., peanut processing, bakeries, a brewery, and a tannery). Other manufacturing activities include soap, soft drinks, and clothing.[31]
Previously, the United Kingdom and other EU countries constituted the major Gambian export markets. However, in recent years Senegal, the United States, and Japan have become significant trade partners of the Gambia. In Africa, Senegal represented the biggest trade partner of the Gambia in 2007, which is a defining contrast to previous years that had Guinea-Bissau and Ghana as equally important trade partners. Globally, Denmark, the United States, and China have become important source countries for Gambian imports. The UK, Germany, Ivory Coast, and the Netherlands also provide a fair share of Gambian imports. The Gambian trade deficit for 2007 was $331 million.[31]
In May 2009, 12 commercial banks existed in the Gambia, including one Islamic bank. The oldest of these, Standard Chartered Bank, dates its presence back to the entry in 1894 of what shortly thereafter became Bank of British West Africa. In 2005, the Swiss-based banking group International Commercial Bank established a subsidiary and now has four branches in the country. In 2007, Nigeria's Access Bank established a subsidiary that now has four branches in the country, in addition to its head office; the bank has pledged to open four more.
In May 2009, the Lebanese Canadian Bank opened a subsidiary called Prime Bank.[33]
-
Serekunda market
-
Brightly-painted fishing boats are common in Bakau
-
The Gambia's wildlife, like this green monkey, attracts tourists
బయటి లింకులు
![]() [[wiktionary:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|నిఘంటువు]] విక్షనరీ నుండి
[[wiktionary:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|నిఘంటువు]] విక్షనరీ నుండి
![]() [[wikibooks:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|పాఠ్యపుస్తకాలు]] వికీ పుస్తకాల నుండి
[[wikibooks:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|పాఠ్యపుస్తకాలు]] వికీ పుస్తకాల నుండి
![]() [[wikiquote:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|ఉదాహరణలు]] వికికోట్ నుండి
[[wikiquote:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|ఉదాహరణలు]] వికికోట్ నుండి
![]() [[wikisource:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|వికీసోర్సు నుండి]] వికీసోర్సు నుండి
[[wikisource:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|వికీసోర్సు నుండి]] వికీసోర్సు నుండి
![]() [[commons:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|చిత్రాలు, మీడియా]] చిత్రాలు, మీడియా నుండి
[[commons:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|చిత్రాలు, మీడియా]] చిత్రాలు, మీడియా నుండి
![]() [[wikinews:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|వార్తా కథనాలు]] వికీ వార్తల నుండి
[[wikinews:Special:Search/{{{1}}}|వార్తా కథనాలు]] వికీ వార్తల నుండి
- ప్రభుత్వం
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 మూస:StateDept
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "The Gambia". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ↑ Gambia changed its name to "The Gambia" because Americans were allegedly confusing Gambia with Zambia. Little evidence for this alleged confusion was ever offered. The presence of the "The" would somehow rectify this confusion.[ఆధారం చూపాలి]
- ↑ Hoare, Ben. (2002) The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia, Kingfisher Publications. p. 11. ISBN 0-7534-5569-2.
- ↑ Hughes, Arnold (2008) Historical Dictionary of the Gambia. Scarecrow Press. p. xx. ISBN 0810862603.
- ↑ Wiseman, John A. (2004) Africa South of the Sahara 2004 (33rd edition): The Gambia: Recent History, Europa Publications Ltd. p. 456.
- ↑ Maclean, Ruth (21 January 2017). "Yahya Jammeh leaves the Gambia after 22 years of rule". The Guardian (in బ్రిటిష్ ఇంగ్లీష్). ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 17 May 2017.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Gambia's Yayah Jammeh confirms he will step down". Al Jazeera. 20 January 2017. Retrieved 21 January 2017.
- ↑ Ramsay, Stuart (22 January 2017). "Former Gambia leader Yahya Jammeh flies into political exile" (in English). Sky News. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
{{cite news}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ 10.0 10.1 "The Gambia overview". World Bank. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ↑ Easton P (1999) "Education and Koranic Literacy in West Africa". IK Notes on Indigenous Knowledge and Practices, n° 11, World Bank Group. pp. 1–4
- ↑ Yevstratyev, O (2018). "Chronological Dating of the Duchy of Courland's Colonial Policy" (PDF). Latvijas Vēstures Institūta Žurnāls. 3: 34–72.
- ↑ Park, Mungo Travels in the Interior of Africa v. II, Chapter XXII – War and Slavery.
- ↑ Webb, Patrick (1994). "Guests of the Crown: Convicts and Liberated Slaves on Mc Carthy Island, the Gambia". The Geographical Journal. 160 (2): 136–142. doi:10.2307/3060072. JSTOR 3060072.
- ↑ Archer, Frances Bisset (1967) The Gambia Colony and Protectorate: An Official Handbook (Library of African Study). pp. 90–94. ISBN 978-0714611396.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 Uppsala Conflict Data Program Gambia. In depth: Economic crisis and a leftist coup attempt in 1981.
- ↑ "UK regrets The Gambia's withdrawal from Commonwealth". BBC News. 3 October 2013. Retrieved 4 October 2013.
- ↑ Gambie : l'opposition désigne Adama Barrow comme candidat unique pour affronter Yahya Jammeh en décembre. Senenews.com (31 October 2016). Retrieved on 18 December 2016.
- ↑ Gambia: Will Mama Kandeh's Nomination Papers Be Accepted? – Freedom Newspaper. Freedomnewspaper.com (6 November 2016). Retrieved on 18 December 2016.
- ↑ "Gambia: Prison sentences for opposition leaders continues downward spiral for human rights". Amnesty International. 20 July 2016.
- ↑ Gambia's Jammeh loses to Adama Barrow in shock election result. BBC News (2 December 2016). Retrieved on 18 December 2016.
- ↑ Gambia leader Yahya Jammeh rejects election result. BBC News (10 December 2016). Retrieved on 18 December 2016.
- ↑ "The Gambia: UK 'very pleased' about Commonwealth return". BBC.
- ↑ "The Gambia presents formal application to re-join the Commonwealth" (Media Release). The Commonwealth. 23 January 2018. Retrieved 24 January 2018.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Boris Johnson is only delighted the Gambia wants back into the British Commonwealth. thejournal.ie (15 February 2017)
- ↑ (http://www.hydrant.co.uk), Site designed and built by Hydrant. "The Gambia rejoins the Commonwealth - The Commonwealth". thecommonwealth.org.
- ↑ Staff, Our Foreign (8 February 2018). "Gambia rejoins the Commonwealth after democratic election" – via www.telegraph.co.uk.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "The Gambia". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- ↑ Wright, Donald (2004). The World and a Very Small Place in Africa: A History of Globalization in Niumi, The Gambia. Armonk, New York: M.E. Sharpe. pp. 149–150. ISBN 978-0-7656-1007-2.
- ↑ Hayward, Derek; J. S. Oguntoyinbo (1987). Climatology of West Africa. Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 189. ISBN 978-0-389-20721-4.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 ఉల్లేఖన లోపం: చెల్లని
<ref>ట్యాగు;bnఅనే పేరుగల ref లలో పాఠ్యమేమీ ఇవ్వలేదు - ↑ Fadera, Hatab (23 April 2012) "Gambia to commence rail system in 2013:- Discloses President Jammeh, as he opens parliament", The Daily Observer (23 April 2012).
- ↑ "Prime Bank (Gambia) is the 12th commercial bank in the Gambia". Observer.gm. 27 May 2009. Archived from the original on 19 July 2014. Retrieved 26 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help)
- మూలాలు చేర్చవలసిన పాఠ్యమున్న వ్యాసాలు
- మూలాలు చేర్చవలసిన పాఠ్యమున్న వ్యాసాలు from January 2017
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- ఆఫ్రికా
- ఆఫ్రికా దేశాలు
- ఆఫ్రికన్ యూనియన్
- కామన్వెల్తు దేశాలు
- ఆర్గనైజేషన్ ఆఫ్ ఇస్లామిక్ కాన్ఫరెన్స్
- మూలాల లోపాలున్న పేజీలు
- May 2009 నుండి మూలాలు చేర్చవలసిన పాఠ్యమున్న వ్యాసాలు
- CS1 బ్రిటిష్ ఇంగ్లీష్-language sources (en-gb)
- CS1 maint: unrecognized language




